Product Consultation
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
 Tel: +86-13486478562
Tel: +86-13486478562 FAX: +86-574-62496601
FAX: +86-574-62496601 Email: [email protected]
Email: [email protected] Address: No. 79 West Jinniu Road, Yuyao, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Provice, China
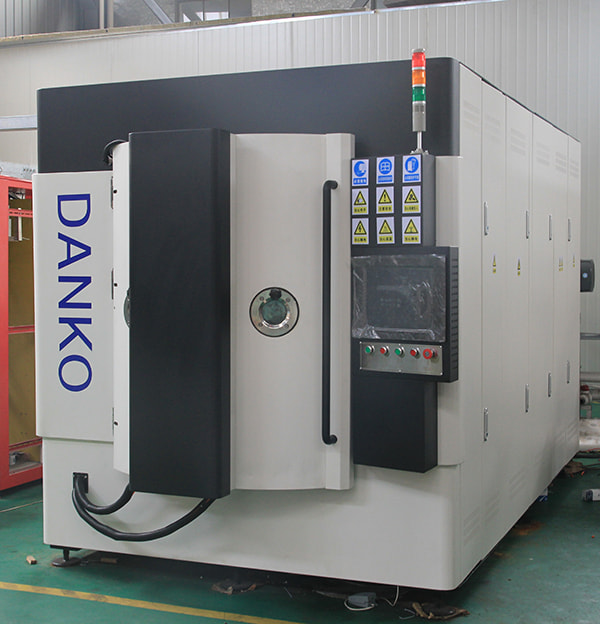
Address: No. 79 West Jinniu Road, Yuyao, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Provice, China OEM/ODM PVD Coater Manufacturers
OEM/ODM PVD Coater Manufacturers