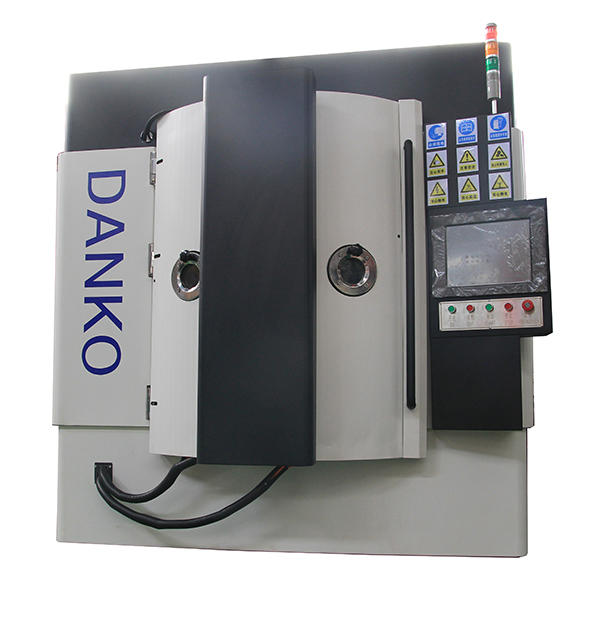
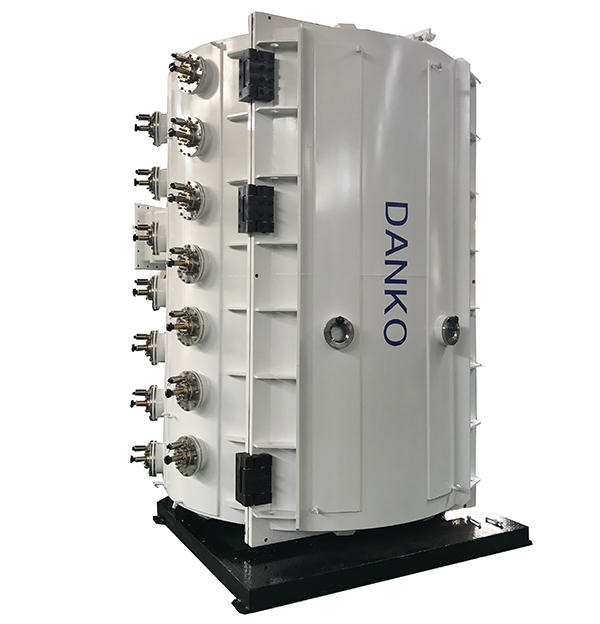
High-End Products PVD Vacuum Coating Machine needs to carry out a series of preparations before starting work, check whether the key components of the equipment such as the vacuum system, heating system, and control system are operating normally, ensure that the equipment is in the condition, place the workpiece to be coated in the vacuum chamber, and ensure that the surface of the workpiece is clean, free of oil and impurities. After the preparation is completed, the equipment starts to evacuate. Through the action of the vacuum pump, the air in the vacuum chamber is gradually extracted until the predetermined vacuum degree is reached. When the vacuum degree reaches the requirement, the equipment starts to heat the metal or alloy target. The target is heated to the evaporation temperature by electron beam, resistance or induction heating. During the heating process, the atoms on the surface of the target gain enough energy to escape and form metal vapor. The metal vapor diffuses freely in the vacuum environment and is transmitted to the surface of the workpiece. During the transmission process, the vapor molecules may collide with the residual gas molecules in the vacuum chamber, but due to the high vacuum degree, the impact of this collision on the vapor is negligible. When the vapor molecules reach the surface of the workpiece, they condense on the surface and form a coating. This process is called vapor deposition. After the coating is completed, the equipment will undergo a cooling process so that the coating can reach a stable state before being removed. After the coating cools down, the vacuum chamber can be opened and the coated workpiece can be taken out. At this point, the surface of the workpiece has been covered with a uniform and dense metal or alloy film with performance.
System Summary
Multi-arc ion & sputtering coatings can be deposited in a wide range of colors. The rang of colors can be further enhanced by introducing reactive gases into the chamber during the deposition process. The widely used reactive gases for decorative coatings are nitrogen, oxygen, argon or acetylene. The decorative coatings are produced in a certain color range, depending on the metal-to-gas ratio in the coating and the structure of the coating. Both of these factors can be altered by changing the deposition parameters.
Prior to deposition, the parts are cleaned so the surface is free of dust or chemical impurities. Once the coating process has started, all the relevant process parameters are continuously monitored and controlled by an automatic computer control system.
• Substrate Material: Glass, Metal (carbon steel, stainless steel, brass), Ceramics, Plastic, Jewelry.
• Structure Type: Vertical structure, #304 Stainless Steel.
• Coating Film: Multi-functional metal film, composite film, transparent conductive film, reflectance-increasing film, electromagnetic shielding film, decorative film.
• Film Color: multi colors, gun black, titanium golden color, rose golden color, stainless steel color, purple color, dark black, dark blue and other more colors.
• Film type: TiN, CrN, ZrN, TiCN, TiCrN, TiNC, TiALN and DLC.
• Consumables in production: Titanium, Chromium, Zirconium, Iron, alloy target; plane target, cylindrical target, twin target, opposite target.
APPLICATION:
• Glassware, such as glass cup, glass lamps, glass artworks.
• Plastic Phone Shell, Phone Parts.
• Mosaic Tile.
• Electron Industry, such as EMI film.
• Watches parts, like watch case and belt.
• Table wares, like metal forks and knives.
• Golf wares, like golf head, golf pole and golf balls.
• Sanitary Products/bathroom wares.
• Door handles & locks.
• Metal jewelry.

 Email:
Email:  Tel:+86-13486478562
Tel:+86-13486478562
 Language
Language  Español
Español Português
Português



















 Tel: +86-13486478562
Tel: +86-13486478562 FAX: +86-574-62496601
FAX: +86-574-62496601 Email:
Email:  Address: No. 79 West Jinniu Road, Yuyao, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Provice, China
Address: No. 79 West Jinniu Road, Yuyao, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Provice, China