Technology
- DK Arc Ion coating
- DK DLC hard coating
- DK Optical thin film coating
- DK PVD coating
- DK Sputtering coating
- UV coating production process
- What are the advantages of PVD coating over traditional electroplating?
- What are the characteristics of PVD coating?
- What are the colors of the PVD coating?
- What are the film types of PVD coatings?
Application Categories
- DK Arc Ion coating
- DK DLC hard coating
- DK Optical thin film coating
- DK PVD coating
- DK Sputtering coating
- UV coating production process
- What are the advantages of PVD coating over traditional electroplating?
- What are the characteristics of PVD coating?
- What are the colors of the PVD coating?
- What are the film types of PVD coatings?
- What is the thickness of PVD coating?
- What substrate can PVD arc ion coat on?
Recent news
-

How does the Medical Instrument Coating Machine handle coatings for instruments that require multiple layers or different coating types?
Dec 09,2025 -
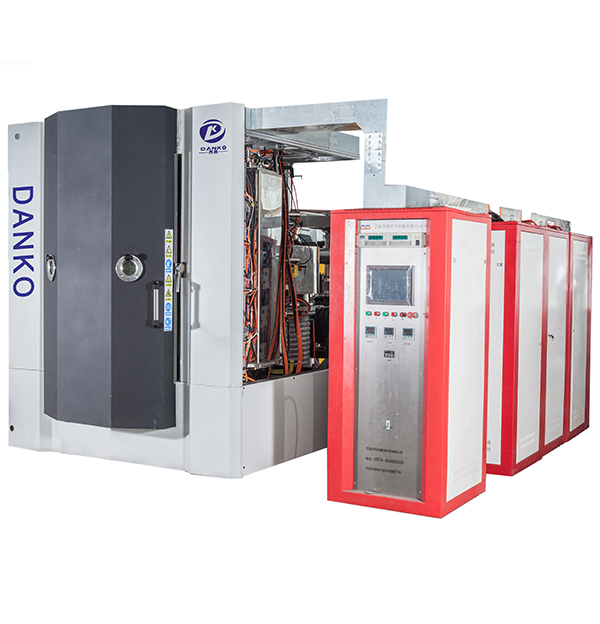

How does the Multi-arc Ion Coating Machine address contamination control within the vacuum chamber to prevent defects?
Dec 02,2025 -
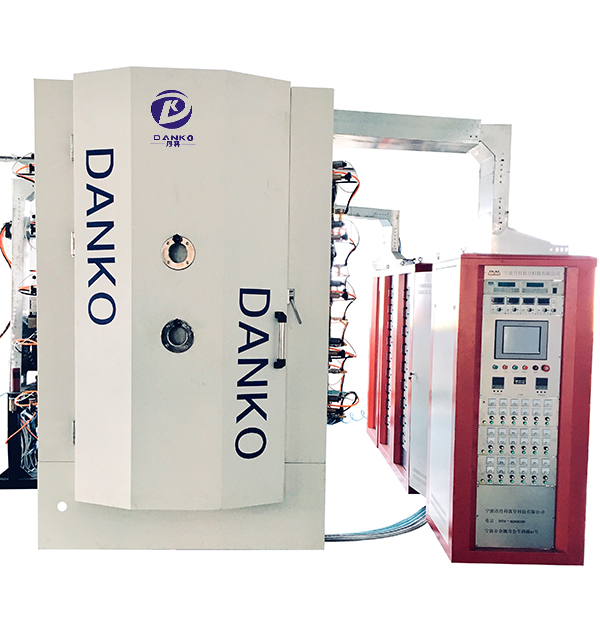

How does the Multi-arc Ion Coating Machine handle high-throughput production and maintain coating quality under rapid processing conditions?
Nov 24,2025
DK Arc Ion coating
Arc Ion Coating
PVD-- physical vapor deposition
One form of physical vapor deposition (PVD coating) is arc ion coating. The history of PVD coating started using arc technology, which has its origin in arc welding.
Targets
The metal to be evaporated is placed as solid block (target) against the inside of a vacuum chamber. A glow discharge is ignited and runs on the target, leaving a footprint. Small spots of a few μm diameter target material are evaporated. The movement of the arc can be guided by magnets.
Plasma coating
The evaporated ionized material is used as plasma coating on a product which rotates inside the vacuum chamber. Arc coatings are used as tool coating and component coating.
Examples of coatings
Examples of arc coating are TiN, AITiN, AICrN, TiSiN, TiCN, CrCN and CrN coating
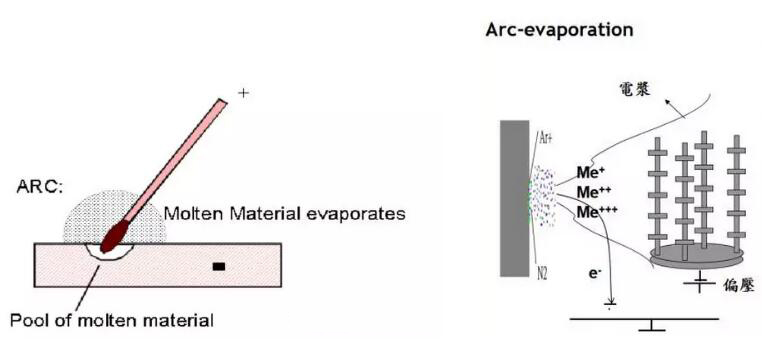
Schematic view of a PVD arc process.
The characterized of Arc coating technology:
High deposition rates (1~3 μm/h) High ionisation, resulting in good adhesion and dense coatings As the target is cooled, little heat to the substrate is generated, even coating at temperatures below 100℃ is possible Several compositions of metals can be evaporated, leaving the remaining solid target unchanged in its composition. The cathodes can be placed in any position (horizontal, vertical, upside down), which makes flexible machine design possible.
The main disadvantages of arc coating technology:
Limited kind of target materials - metals only (no oxides) - which do not have a too low evaporation temperature Due to the high current densities some amount of the target material is ejected as small liquid droplets.
Quick Link
Detailed information
 Tel: +86-13486478562
Tel: +86-13486478562 FAX: +86-574-62496601
FAX: +86-574-62496601 Email: [email protected]
Email: [email protected] Address: No. 79 West Jinniu Road, Yuyao, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Provice, China
Address: No. 79 West Jinniu Road, Yuyao, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Provice, China
 OEM/ODM PVD Coater Manufacturers
OEM/ODM PVD Coater Manufacturers

 Email:
Email:  Tel:+86-13486478562
Tel:+86-13486478562
 Language
Language  Español
Español Português
Português